Irrigation systems that are inefficient or stretched can waste a significant amount of water.
In Part 10 of our Drought Solutions video series, you'll discover why the right spray nozzle can greatly increase the efficiency of your customer's irrigation system, the key to using both sprays and rotors on the same system, and a simple way to balance pressure when there's no pressure or volume at the furthest heads.
Video Transcript
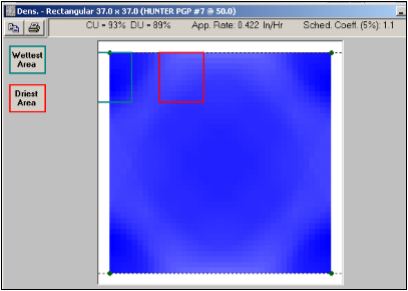
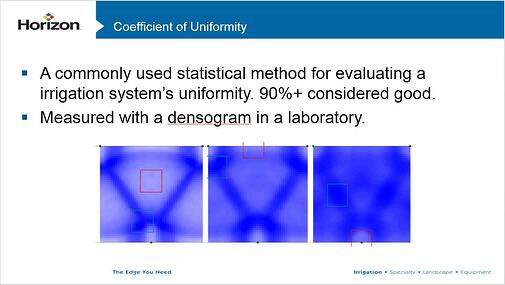
We were talking about DU. DU on a sprinkler head. If you get anywhere near 75% - that's distribution uniformity. That's how that one sprinkler head works. You get somewhere near 75%, that's a great, great head.
You take a great sprinkler head at 75% and you put it in a great designed irrigation system. We already know that we can get to 90% water efficiencies. 93%. 95%. That's what we're looking for on every single system.

Here's the MP Rotator. Here's the Toro Precision Nozzles. You got the Rain Bird Rotary Nozzles. These are all super efficient sprinkler heads because they are evenly matched precip rates. These are already done for us. It's not like your gear drive rotor.
They're all available in radiuses from about 5' to 27'. You're going to use less water. Like up to a third.
Matching Precipitation Rates of Sprays and Rotors
This has a precip rate of .5" an hour. Same exact precip rate as a gear drive rotor. So now you can mix this spray head with a gear drive rotor on the same system because their precip rates are the same.
Cool opportunity. So now instead of having a gear drive rotor shoot all the way across 3 areas and back, you can put this on and get that smaller area taken care of on the same system.
So you got a precip rate of .5" an hour. what's the standard precip rate rate of a spray nozzle? Fixed arc spray. 1.5" an hour. This is 3 times more efficient. So on stretched or zones that have pressure problems, this is a great retrofit because they use that much less water.
A Simple Way to Regulate Pressure Throughout Your System
How many spray heads do you see on systems? I see systems pop up and there's 40 spray heads on it, especially in medians. You start counting them and you go, man that's gotta have a 4" main sitting underneath it. To get the water all the way down there.
Super, super inefficient systems. A lot of times they're so inefficient, by the time you get to the other end, there's no water.
So let's say there's no water at the other end. Because we've got great pressure here, but by the time we get all the way down there, we don't have any pressure or volume. Because they didn't pipe size. That's a whole other class, but anyhow.
They don't have any pressure at the other end, so what can we do?
On a spray system, if we just go and put PRS stems in. Pressure regulating stems. Now the pressure here, instead of being 80 and it being 10 down at the other end.
Now we just retrofitted that system and it balanced that whole system and made it right.
Now it's 30, 30, 30, 30, 30, and you stretch that pressure down to the other end. Let's go ahead and put something on now that instead of using 1.5" of water an hour, only uses .5" of water.
Now we just retrofitted that system and it balanced that whole system and made it right. This is great for retrofit systems that are stretched. These are great products for that.
When they originally came out, they came out for new installs. New install, new install, new install.
It's like, wait a minute. These are retrofit issues right here. All solved with one. And not one of these, do you have to pull out a shovel to fix. It's an internal gut change.
If we're going to do the pressure regulator and we're going to do the nozzle, we might as well put the check valve in the bottom. And it's an easy, you just go along and you gut cans. And you just retrofitted a whole system. And the water savings you'll see this afternoon. Huge. Huge water savings.








 As irrigation and landscape professionals, you know the benefits of using smart water products - reduction in water usage, healthier soil, lower water bills.
As irrigation and landscape professionals, you know the benefits of using smart water products - reduction in water usage, healthier soil, lower water bills.